- “Lighthouse Factory”, the Beacon for Intelligent Manufacturing Unveiled
Introduction: Why "lighthouse Factory" are becoming popular worldwide?

In the deep night at sea, lighthouses guide ships to safety; similarly, amidst the wave of digital transformation in manufacturing, the “Lighthouse Factory” is becoming the guiding beacon that global enterprises fiercely pursue. The “Lighthouse Factory” network, jointly created by the World Economic Forum (WEF) and McKinsey in 2018, not only represents the pinnacle of Industry 4.0 in manufacturing but also holds the key to resolving challenges within the industry.
The author, Mr. Haoliang Zhu, an expert with 20 years of experience in digital factory planning, will unveil the mysteries of the “Lighthouse Factory” from six dimensions: origin of the concept, current development status, core types, application strategies, unique value, and the lighthouse effect—combined with practical experiences. A case study on local lighthouse factories in China is included at the end, filled with valuable insights for easy understanding!
I. Origin of the Lighthouse: The “Past and Present”
As digital technologies rapidly advance, the manufacturing industry is undergoing profound changes. To promote the digital transformation of global manufacturing, the World Economic Forum and McKinsey launched the “Lighthouse Factory” project in 2018. This initiative aims to identify and recognize factories that have pioneered the adoption of advanced manufacturing technologies and achieved significant results in the Fourth Industrial Revolution. These factories are regarded as the “lighthouses” of their industries, providing exemplary models for the digital transformation of other enterprises.Since the first nine globally advanced factories were selected in September 2018—showcasing successful cases of digital transformation—new factories continue to join the global lighthouse network annually. As of October 8, 2024, the number of global lighthouse factories has reached 172, spanning 35 different industries across 31 countries. Among them, China boasts 74 lighthouse factories, accounting for 43%, leading the world. This achievement underscores China's strong emphasis and support for the transformation and upgrading of its manufacturing sector, as well as the proactive exploration and practice of Chinese enterprises in technological innovation, intelligent manufacturing, and sustainable development.
Being recognized as a “Global Lighthouse Factory” is akin to receiving an “Oscar” award in the industrial field. Companies that earn this accolade not only possess outstanding production capabilities but also play a pivotal role in demonstrating and guiding upstream and downstream enterprises within the supply chain toward intelligent transformation, thereby enhancing the overall level of new industrialization.
What is a lighthouse factory? A lighthouse factory refers to a “future factory” that extensively applies Industry 4.0 technologies (such as AI, IoT, and digital twins) throughout its manufacturing and operational processes and achieves breakthrough results in production efficiency, sustainability, agility, and more. Lighthouse factories are characterized by holistic optimization (not just point innovations), replicability (experience can be replicated), and a balance of economic and social value.
The symbolic significance of “Lighthouse Factories” is to illuminate the path for other businesses in their digital transformation journey, helping them avoid “running aground” in the fog of technology.

2. Current Status of Lighthouses
As of October 2024, a total of 172 lighthouse factories have been evaluated globally, among which China accounts for 74, representing 43%, maintaining its position as the world's leader in both quantity and proportion.
The latest evaluation in October 2024 identified 22 factories distributed across 10 countries, including China, the Czech Republic, and Germany, with 13 factories from China, the highest number.
In this evaluation of "lighthouse factories," 17 are classified as "single factory lighthouses," focusing on enhancing efficiency at the individual factory level; 2 are "end-to-end lighthouses," mainly reflecting extensive deployment of technology across the upstream and downstream of the value chain to achieve cost reduction and efficiency improvement on a large scale. Additionally, 3 "sustainable lighthouses" represent the latest achievements in green manufacturing. All three of these "sustainable lighthouse" factories are located in China. Through the application of technologies such as artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things (IoT), as well as other process innovations, these companies have achieved reductions of over 20% in metrics like direct carbon emissions and indirect energy carbon emissions, leading the world. Below is the list of "lighthouse factories" for 2024 published by the World Economic Forum (China section).
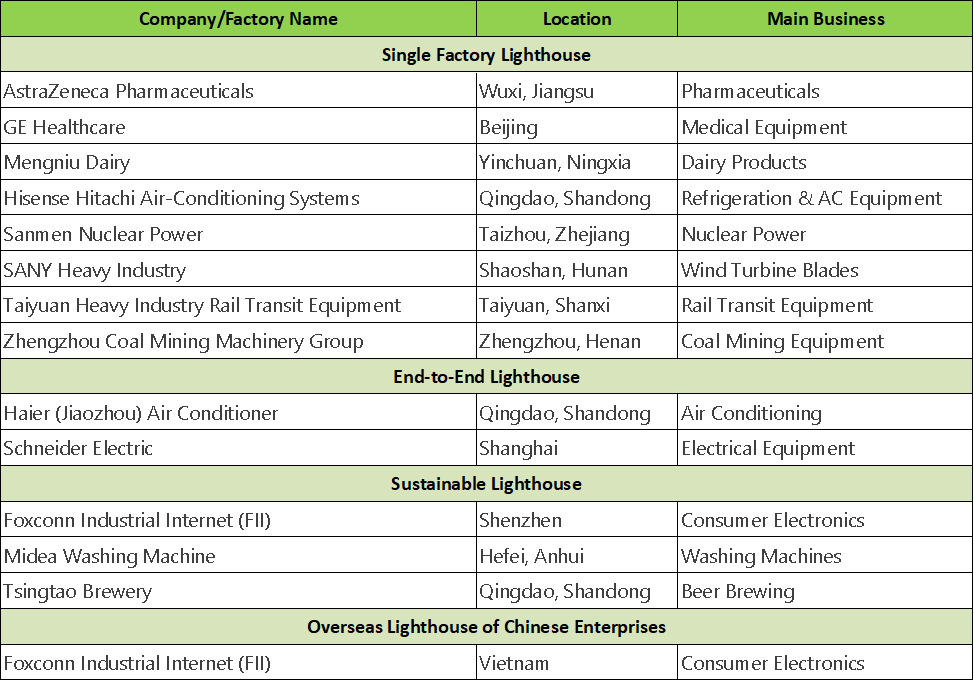
In this selection of lighthouse factories, Chinese companies performed remarkably. Below, one company from each category of lighthouses is described to facilitate understanding of what different types of lighthouse factories have accomplished (typical cases).
End-to-End Lighthouse: Haier (Jiaozhou) Air Conditioning (Qingdao, China): To meet the rapidly increasing global demand and address delays in R&D, delivery, and after-sales service, Haier (Jiaozhou) Air Conditioning, which supplies 90% of its products globally, adopted technologies such as big data, advanced algorithms, and generative artificial intelligence to optimize the entire value chain, shortening the design cycle by 49%, reducing order delivery time by 19%, and decreasing overseas market failure rates by 28%.
Single Factory Lighthouse: SANY Heavy Energy (Shaoshan, China): To tackle various challenges in the production and transportation of large wind turbine blades, SANY Heavy Energy deployed 29 use cases of Fourth Industrial Revolution technologies, including artificial intelligence and intelligent automation, which reduced product defects by 20%, increased production efficiency by 33%, and shortened delivery time by 34%, demonstrating the significant impact of digital technology on clean energy development.
Sustainable Lighthouse: Foxconn Industrial Internet (Shenzhen, China): To fulfill carbon neutrality commitments in the consumer electronics industry, Foxconn Industrial Internet employed artificial intelligence, IoT, and other Fourth Industrial Revolution technologies to optimize material recycling, track real-time carbon footprints, and advance process innovations for sustainable development. This resulted in a 42% reduction in Scope 3 emissions, a 24% reduction in Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions, and an increase in recyclable material content to 55%-75%.
Trends: Transition from "Manufacturing" to "Smart Manufacturing"
The determination of China's manufacturing industry to digitally transform is a key factor driving the rapid growth of the number of lighthouse factories. In recent years, China has vigorously promoted the high-quality development of the manufacturing industry, and encouraged enterprises to accelerate the pace of digital transformation through policy guidance, financial support and technological innovation. This top-down driving force provides a solid policy guarantee and a good development environment for the emergence of lighthouse factories in China.
The proactive exploration and practices of Chinese enterprises in the field of intelligent manufacturing have also provided rich cases and experiences for the birth of lighthouse factories. By applying advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, IoT, and big data, these enterprises have achieved intelligent, automated, and efficient production processes, not only improving production efficiency and product quality but also reducing energy consumption and environmental pollution. The demonstrative effect of these successful cases further inspires enthusiasm and motivation for the transformation of China's manufacturing industry toward smart manufacturing.
3. Five Lighthouse Types
Based on the depth of technology application and scenario differences, lighthouse factories can be divided into four types before 2024:
3-1. Efficiency-Driven Type
l Core Goal: Extreme cost reduction and efficiency enhancement.
l Technology Combination: Automated production lines + AI predictive maintenance + Digital performance management.
l Representative Case: Siemens (Chengdu) Factory, where Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) increased to 90%.
3-2. Agile Response Type
l Core Goal: Rapid response to market demand fluctuations.
l Technology Combination: Flexible manufacturing systems + Real-time supply chain collaboration + Customer data platforms.
l Representative Case: Johnson & Johnson (Xi'an) Medical Devices Factory, with order response speed increased by 60%.
3-3. End-to-End Value Chain Type
l Core Goal: Unifying the entire link from R&D to service.
l Technology Combination: Digital twin + Consumer-to-Manufacturing (C2M) + Blockchain traceability.
l Representative Case: Haier KAOS Platform, supporting user-customized refrigerators with delivery in 7 days.
3-4. Sustainable Development Type
l Core Goal: Green manufacturing and circular economy.
l Technology Combination: Energy management systems + Waste AI monitoring + Carbon footprint tracking.
l Representative Case: Unilever (Hefei) Ice Cream Factory, where water consumption per unit product decreased by 50%.
3-5. Talent Development
l In 2025, a new type of lighthouse factory focusing on "Talent Development" was added.
l Core Goal: Aimed at encouraging enterprises that empower employees with advanced technologies, improve on-site safety and environment, optimize talent selection, training, application, and retention, thereby significantly enhancing efficiency.
4. Application Guide: How Do Enterprises Apply for Lighthouse Factories?
The evaluation criteria for "Lighthouse Factories" include possessing all the essential characteristics of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, specifically including technologies such as automation, Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), digitization, big data analytics, and 5G. It is crucial to establish a digital system that covers the entire internal process of the enterprise, all links of the upstream and downstream supply chain, and the entire lifecycle of products and services, thereby comprehensively enhancing the efficiency of the enterprise and its supply chain while reducing costs. At the same time, by leveraging data elements, new models can be explored to create new growth points with significant results.
During the entire selection process, the expert evaluation meeting plays a very important role. The final list of selected Lighthouse Factories is determined by expert voting, and since each expert has different focus areas, it is difficult to have a clear scoring system like some authoritative selections within the country. The second point concerns obtaining scalability benefits, where technologies that are relatively mature, or have undergone long-term market testing or continuous iteration and optimization are particularly welcomed; concurrent to this, the technology must bring significant scalability benefits to the operations and financial indicators of enterprises or factories.
9-Step Application Process:
(1) Submit Application Questionnaire: Visit the Global Lighthouse Network application questionnaire (application URL: initiatives.weforum.org/global-lighthousenetwork/home ) to apply for Lighthouse Factory nomination, explaining how the factory utilizes advanced technologies and creates value.
(2) Review Factory Applications: The World Economic Forum will conduct an internal review to determine if the applying factory is sufficiently mature in its digital transformation to be a strong candidate for a Lighthouse Factory.
(3) Arrange On-Site Visit: If selected for an on-site visit, the World Economic Forum's evaluation team will contact the factory to arrange the site visit and explain how to prepare for the pre-visit report
(4) Prepare Pre-Visit Report: Prior to the delegation’s on-site visit, the applying factory needs to prepare a pre-visit report according to requirements, providing more details about the technology applications of the candidate Lighthouse Factory.
(5) Organize On-Site Visit: The World Economic Forum will send an evaluation team for a one-day on-site visit to review technology application cases and interview with the core reception staff.
(6) Complete Final Report: The World Economic Forum will present the final report template to the factory, which should refine and complete the final report based on the evaluation team's feedback.
(7) Expert Group Assessment: The World Economic Forum will randomly select experts from the forum's global expert resource pool to form a neutral expert group comprised of academia, industry, and technology pioneers to assess all applicants and select those to be recognized as Lighthouse Factories.
(8) Notify Evaluation Results: The World Economic Forum will inform the final decision of the expert group.
(9). Announce Lighthouse Factories: The World Economic Forum will announce the selected Lighthouse Factories at significant annual conference events.
5. The "Unique Skills" of Lighthouse Factories
Kiva Allgood, the head of the Advanced Manufacturing and Supply Chain Center at the World Economic Forum, stated that lighthouse factories are breaking through the noise brought by artificial intelligence, continuously raising the standards for digital transformation. They apply advanced technologies to business operations, not only to improve production efficiency but also to create an inclusive and sustainable future for employees and society.
According to disclosures from the World Economic Forum, the latest selected lighthouse factories have increased labor productivity by an average of 50%, thanks to various digital solutions they implemented, such as interactive training programs, smart devices, and wearable technology, as well as automated systems that integrate robotics, artificial intelligence, and machine vision technology. Process modeling and root cause analysis technologies have also enhanced the efficiency of the end-to-end supply chain in lighthouse factories, resulting in average reductions in energy consumption, inventory, and waste by 22%, 27%, and 55%, respectively.
“Artificial intelligence plays an increasingly important role in Industry 4.0, becoming a key driving force in reshaping global manufacturing,” said Zheng Hongmeng, Chairman and General Manager of Foxconn Industrial Internet (FII).
In this selection, two factories from FII made the list. The Shenzhen Guanlan factory of FII was recognized as a "Sustainable Lighthouse Factory," becoming the first in Guangdong Province. Its factory in Bac Ninh, Vietnam, was selected as a "Lighthouse Factory," marking it as Vietnam's first "Lighthouse Factory." Additionally, the Taiyuan factory of Taiyuan Heavy Industry, empowered by FII services, and the Hisense Hitachi factory in Qingdao also successfully made the list. Currently, the number of "Lighthouse Factories" created by FII through external empowerment has increased to five.
According to the World Economic Forum's evaluation of the FII Guanlan factory, in order to fulfill the carbon neutrality commitment of the consumer electronics industry, FII adopted artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things, and other Fourth Industrial Revolution technologies to optimize material recycling, track real-time carbon footprints, and promote process innovation to achieve sustainable development, significantly reducing carbon emissions and increasing the proportion of recyclable materials to 55%-75%.
AI-driven technological innovation has become an important support for FII's sustainable development strategy. Wu Yanru, the project leader for the sustainable lighthouse project at the Guanlan factory, introduced that by deploying advanced use cases based on process flow and IoT for carbon footprint optimization, AI-driven sustainable anodic processes, recycling of raw materials in the value chain, and lean improvements, the Guanlan factory has successfully achieved optimal synergy between capacity growth and reduced carbon emissions.

6.Lighthouse Effect: How to Illuminate the Entire Manufacturing Industry?
6-1. Technology Dissemination: From "One Blooming Alone" to "A Hundred Trees Competing in Spring"
The advanced technology of lighthouse factories has never been a "secret recipe." Taking CATL as an example, this global power battery giant not only uses AI quality inspection systems in its own factories but also opens it up to upstream and downstream suppliers. By sharing algorithm models and defect databases, the efficiency of battery separator inspections for suppliers improved by 40%, and the quality issue rate dropped from 500 parts per million to 50. This "technology transfusion" directly drives the overall upgrade of the industry chain, forming an ecosystem of "CATL + 100 intelligent suppliers."
After SANY Heavy Industry's Beijing pile driver factory was selected as a lighthouse, it distilled its digital transformation experience into a replicable "toolbox," including smart scheng systems, equipment health management platforms, etc., and quickly promoted it to 15 domestic brother factories. Just the Changsha pump truck factory alone achieved a doubling of production capacity and a 30% reduction in energy consumption using this set of experiences. This "point-to-surface" diffusion effect allows advanced manufacturing models to grow from "bonsai-style pilots" to truly become "forest-level ecosystems."
6-2. Ecological Co-construction: Cross-industry Collaborative Networks - When Car Manufacturers and Mobile Phone Manufacturers Start to "Exchange Brains"
The ultimate form of digital transformation is the "technological community" that breaks industry barriers. In the Yangtze River Delta, a certain new energy vehicle brand collaborates with a consumer electronics company to build a digital twin platform, achieving remarkable cross-border collaboration effects: automotive engineers import body structure simulation models into the platform, while mobile phone manufacturers contribute chip heat dissipation simulation data. The two sides cross-validate through AI algorithms, compressing the research and development cycle of a new electric vehicle's battery thermal management from 18 months to 11 months.
This collaborative model of "you contain me" even gives rise to new business models. A home appliance company connects its flexible production line with the 3D measurement data from a clothing company, launching a "customized refrigerator" service—consumers upload their kitchen dimensions, and the factory directly generates a customized refrigerator size, with cabinet installation gaps even measured to the millimeter level. As noted in a McKinsey report: "In the next decade, 30% of manufacturing innovation will come from cross-industry technology integration."
6-3. Policy Promotion: Countries Competing for Layout - The "Lighthouse Competition" in Global Manufacturing
When China included lighthouse factories in its "14th Five-Year Plan" as a key project for new infrastructure and supported it with a hundred billion-level intelligent manufacturing special fund, Germany immediately ramped up its "Industry 4.0" 2.0 strategy, announcing plans to cultivate 1,000 lighthouse-level enterprises by 2030 and offering a 15% tax reduction on digital equipment purchases for selected companies. Behind this smoke-free competition is the struggle for discourse power in manufacturing among countries.
Chinese local governments are also playing a combination of cards: some cities offer rewards of 4 to 20 million yuan to newly established lighthouse factories, equivalent to two years' investment in digital transformation for enterprises; the Guangzhou Development Zone has launched the "Lighthouse Mentor Program," inviting companies like Haier and Midea to provide free technical diagnostics for SMEs. Meanwhile, across the Pacific, the U.S. is indirectly supporting local lighthouse factories through the "Chips and Science Act," requiring subsidized companies to achieve 80% digital coverage of production processes.
Policy dividends are triggering a chain reaction. According to incomplete statistics, in 2023, global manufacturing enterprises’ digital investment surged by 45% year-on-year, with 70% of companies explicitly stating they aim to meet lighthouse factory standards. This "Lighting Movement," jointly promoted by governments, enterprises, and think tanks, has become a key variable in reshaping the global manufacturing landscape.
Conclusion: After the Lighthouse, the Future has Arrived
Lighthouse factories are not just testing grounds for technology, but also a reshaping of the manufacturing industry's values — shifting from a pursuit of scale to a pursuit of excellence, and from relying on human labor to embracing human-machine collaboration.
As Jeremy Jurgens, Executive Director of the World Economic Forum, stated: "The significance of lighthouse factories lies not in their selection, but in their demonstration — proving to the world that digital transformation is not a multiple-choice question, but a matter of survival."
References:
1. World Economic Forum "Global Lighthouse Network White Paper" (2023)
2. McKinsey "Digital Transformation in Manufacturing: Insights from Lighthouse Factories"
3. Ministry of Industry and Information Technology of China "Intelligent Manufacturing Development Index Report"







